In this Spring security oauth2 tutorial, learn to build an authorization server to authenticate your identity to provide access_token, which you can use to request data from resource server.
1. Introduction to OAuth 2
OAuth 2 is an authorization method to provide access to protected resources over the HTTP protocol. Primarily, oauth2 enables a third-party application to obtain limited access to an HTTP service –
- either on behalf of a resource owner by orchestrating an approval interaction between the resource owner and the HTTP service
- or by allowing the third-party application to obtain access on its own behalf.
1.1. Roles
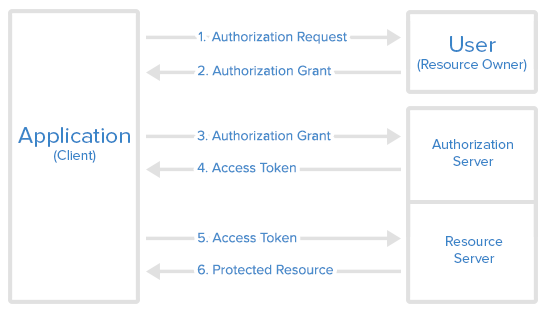
OAuth defines four roles –
- Resource Owner – The user of the application.
- Client – the application (user is using) which require access to user data on the resource server.
- Resource Server – store user’s data and http services which can return user data to authenticated clients.
- Authorization Server – responsible for authenticating user’s identity and gives an authorization token. This token is accepted by resource server and validate your identity.
1.2. Access Token vs Refresh Token
An access token is a string representing an authorization issued to the client. Tokens represent specific scopes and durations of access, granted by the resource owner, and enforced by the resource server and authorization server.
Refresh token is issued (along with access token) to the client by the authorization server, and it is used to obtain a new access token when the current access token becomes invalid or expires. The refresh token is also used to get additional access tokens with identical or narrower scope (access tokens may have a shorter lifetime and fewer permissions than authorized by the resource owner). Issuing a refresh token is optional at the discretion of the authorization server.
- The responsibility of access token is to access data before it gets expired.
- The responsibility of refresh token is to request for a new access token when the existing access token is expired.
2. Oauth2 – Authorization Server
To create authorization server using spring security oauth2 module, we need to use annotation @EnableAuthorizationServer and extend the class AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter.
import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.configurers.ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableAuthorizationServer;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configurers.AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer;@Configuration@EnableAuthorizationServerpublic class OAuth2AuthorizationServer extends AuthorizationServerConfigurerAdapter { @Autowired private BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder; @Override public void configure(AuthorizationServerSecurityConfigurer security) throws Exception { security .tokenKeyAccess("permitAll()") .checkTokenAccess("isAuthenticated()") .allowFormAuthenticationForClients(); } @Override public void configure(ClientDetailsServiceConfigurer clients) throws Exception { clients .inMemory() .withClient("clientapp").secret(passwordEncoder.encode("123456")) .authorizedGrantTypes("password", "authorization_code", "refresh_token") .authorities("READ_ONLY_CLIENT") .scopes("read_profile_info") .resourceIds("oauth2-resource") .accessTokenValiditySeconds(120) .refreshTokenValiditySeconds(240000); }} |
- Spring security oauth exposes two endpoints for checking tokens (
/oauth/check_tokenand/oauth/token_key) which are by default protected behinddenyAll(). tokenKeyAccess() and checkTokenAccess() methods open these endpoints for use. ClientDetailsServiceConfigureris used to define an in-memory or JDBC implementation of the client details service. we have used in-memory implementation. It has following important attribute:clientId – (required) the client id.
secret – (required for trusted clients) the client secret, if any.
scope – The scope to which the client is limited. If the scope is undefined or empty (the default), the client is not limited by scope.
authorizedGrantTypes – Grant types that are authorized for the client to use. The default value is empty.
authorities – Authorities that are granted to the client (regular Spring Security authorities).
redirectUris – redirects the user-agent to the client’s redirection endpoint. It must be an absolute URL.
3. Oauth2 – Resource Server
To create resource server component, use @EnableResourceServer annotation and extend the ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter class.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.EnableResourceServer;import org.springframework.security.oauth2.config.annotation.web.configuration.ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter;@Configuration@EnableResourceServerpublic class OAuth2ResourceServer extends ResourceServerConfigurerAdapter { @Override public void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/api/**").authenticated() .antMatchers("/").permitAll(); }} |
Above config enable protection on all endpoints starting /api. All other endpoints can be accessed freely.
The resource server also provides a mechanism to authenticate users themselves. It will be a form-based login in most cases.
import org.springframework.context.annotation.Bean;import org.springframework.context.annotation.Configuration;import org.springframework.core.annotation.Order;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.authentication.builders.AuthenticationManagerBuilder;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.builders.HttpSecurity;import org.springframework.security.config.annotation.web.configuration.WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter;import org.springframework.security.crypto.bcrypt.BCryptPasswordEncoder;@Configuration@Order(1)public class SecurityConfig extends WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter { @Override protected void configure(HttpSecurity http) throws Exception { http .antMatcher("/**") .authorizeRequests() .antMatchers("/oauth/authorize**", "/login**", "/error**") .permitAll() .and() .authorizeRequests() .anyRequest().authenticated() .and() .formLogin().permitAll(); } @Override protected void configure(AuthenticationManagerBuilder auth) throws Exception { auth .inMemoryAuthentication() .withUser("humptydumpty").password(passwordEncoder().encode("123456")).roles("USER"); } @Bean public BCryptPasswordEncoder passwordEncoder(){ return new BCryptPasswordEncoder(); }} |
Above WebSecurityConfigurerAdapter class setup a form based login page and open up the authorization urls with permitAll().
4. Oauth2 protected REST resources
For demo purpose, I have created only one API which returns the logged in user’s name and email.
import org.springframework.http.ResponseEntity;import org.springframework.security.core.context.SecurityContextHolder;import org.springframework.security.core.userdetails.User;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;@Controllerpublic class RestResource { @RequestMapping("/api/users/me") public ResponseEntity<UserProfile> profile() { //Build some dummy data to return for testing User user = (User) SecurityContextHolder.getContext().getAuthentication().getPrincipal(); String email = user.getUsername() + "@howtodoinjava.com"; UserProfile profile = new UserProfile(); profile.setName(user.getUsername()); profile.setEmail(email); return ResponseEntity.ok(profile); }} |
public class UserProfile { private String name; private String email; //Setters and getters @Override public String toString() { return "UserProfile [name=" + name + ", email=" + email + "]"; }} |
5. Demo
We have an API http://localhost:8080/api/users/me, which we can access by directly putting username/password in the login form, but third party application cannot access the API as we do in browsers. They need an oauth2 token.
5.1. Get authorization grant code from user
As shown in the above sequence diagram, the first step is to get authorization grant from resource owner from URL : http://localhost:8080/oauth/authorize?client_id=clientapp&response_type=code&scope=read_profile_info
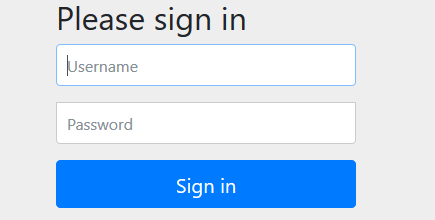
It will bring a login page. Provide a username and password. For this demo, use “humptydumpty” and “123456”.
After login, you will be redirected to the grant access page where you choose to give access to third party applications.
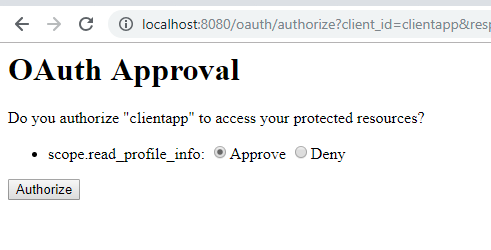
It will redirect to a URL like : http://localhost:8081/login?code=EAR76A. Here 'EAR76A' is authorization code for the third party application.
5.2. Get access token from authorization server
Now the application will use an authorization grant to get the access token. Here we need to make the following request. Use the code obtained in the first step here.
http://localhost:8080/oauth/tokenHeaders:Content-Type: application/x-www-form-urlencodedauthorization: Basic Y2xpZW50YXBwOjEyMzQ1Ng==Form data - application/x-www-form-urlencoded:grant_type=authorization_codecode=EAR76Aredirect_uri=http://localhost:8081/login |
It will ask for client app credentials in a separate window.
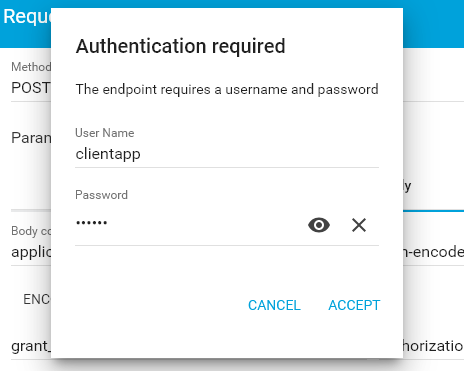
Or make a similar request from cURL.
curl -X POST --user clientapp:123456 http://localhost:8081/oauth/token -H "content-type: application/x-www-form-urlencoded" -d "code=FfrzTj&grant_type=authorization_code&redirect_uri=http%3A%2F%2Flocalhost%3A8082%2Flogin&scope=read_user_info" |
{ "access_token": "59ddb16b-6943-42f5-8e2f-3acb23f8e3c1", "token_type": "bearer", "refresh_token": "cea0aa8f-f732-44fc-8ba3-5e868d94af64", "expires_in": 4815, "scope": "read_profile_info"} |
5.3. Access user data from resource server
Once we have the access token, we can go to the resource server to fetch protected user data.
Hit the following request:
curl -X GET http://localhost:8080/api/users/me -H "authorization: Bearer 59ddb16b-6943-42f5-8e2f-3acb23f8e3c1" |
It will return the response.
{"name":"humptydumpty","email":"humptydumpty@howtodoinjava.com"} |
6. Maven dependencies for spring security oauth2 app
The pom file used for this spring security 5 oauth2 example is:
<?xml version="1.0" encoding="UTF-8"?> <modelVersion>4.0.0</modelVersion> <parent> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-parent</artifactId> <version>2.1.4.RELEASE</version> <relativePath /> <!-- lookup parent from repository --> </parent> <groupId>com.howtodoinjava</groupId> <artifactId>spring-oauth2-resource-server-demo</artifactId> <version>0.0.1-SNAPSHOT</version> <name>spring-oauth2-resource-server-demo</name> <description>Demo project for Spring Boot</description> <properties> <java.version>1.8</java.version> </properties> <dependencies> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security.oauth.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-oauth2-autoconfigure</artifactId> <version>2.1.8.RELEASE</version> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-web</artifactId> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-starter-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> <dependency> <groupId>org.springframework.security</groupId> <artifactId>spring-security-test</artifactId> <scope>test</scope> </dependency> </dependencies> <build> <plugins> <plugin> <groupId>org.springframework.boot</groupId> <artifactId>spring-boot-maven-plugin</artifactId> </plugin> </plugins> </build></project> |
Drop me your questions in comments.
No comments:
Post a Comment