Internationalization is the process of designing a software application so that it can potentially be adapted to various languages and regions without engineering changes. Localization is the process of adapting internationalized software for a specific region or language by adding locale-specific components and translating text [Wiki]. Spring framework is shipped with LocaleResolver to support the internationalization and thus localization as well. This tutorial will help you in learning how to add internationalization support in your spring mvc based web application.
Table of Contents
1) Adding locale specific message resources
2) Adding LocaleResolver configuration in spring context
3) JSP changes to display locale specific messages
4) Project Structure
5) Testing the Application
6) Other Project Files
Let’s start analyzing the changes which you will need to make for adding i18n support into your spring web application.
1) Adding locale specific message resources
If you want to support multiple locales, then first step is obliviously to have each locale specific properties file having texts in that locale specific language. In our example, I am supporting two locales. First is United States with language English, and second locale is Chinese.
messages.properties
lbl.Id=Employee Idlbl.firstName=First Namelbl.lastName=First Namelbl.page=All Employees in System |
messages_zh_CN.properties
lbl.Id=\u5458\u5DE5IDlbl.firstName=\u540D\u5B57lbl.lastName=\u59D3lbl.page=\u7CFB\u7EDF\u4E2D\u7684\u6240\u6709\u5458\u5DE5 |
Notice the naming convention for these properties files. Locale specific files have locale short-code appended into their name.
2) Adding LocaleResolver configuration in spring context
To make Spring MVC application supports the internationalization, you will need to register two beans.
1. SessionLocaleResolver
SessionLocaleResolver resolves locales by inspecting a predefined attribute in a user’s session. If the session attribute doesn’t exist, this locale resolver determines the default locale from the
accept-language HTTP header.<bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"> <property name="defaultLocale" value="en" /></bean> |
2. LocaleChangeInterceptor
LocaleChangeInterceptor interceptor detects if a special parameter is present in the current HTTP request. The parameter name can be customized with the
paramName property of this interceptor. If such a parameter is present in the current request, this interceptor changes the user’s locale according to the parameter value.<bean id="localeChangeInterceptor" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor"> <property name="paramName" value="lang" /></bean><bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping"> <property name="interceptors"> <list> <ref bean="localeChangeInterceptor" /> </list> </property></bean> |
The complete application context file for this application looks like this:
<beans xmlns="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xmlns:context="http://www.springframework.org/schema/context" xsi:schemaLocation="http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans http://www.springframework.org/schema/beans/spring-beans-3.0.xsd http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/ http://www.springframework.org/schema/context/spring-context-3.0.xsd"> <context:component-scan base-package="com.howtodoinjava.demo" /> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.AnnotationMethodHandlerAdapter" /> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.view.InternalResourceViewResolver"> <property name="prefix" value="/WEB-INF/views/" /> <property name="suffix" value=".jsp" /> </bean> <bean id="messageSource" class="org.springframework.context.support.ResourceBundleMessageSource"> <property name="basename" value="messages" /> </bean> <bean id="localeResolver" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.SessionLocaleResolver"> <property name="defaultLocale" value="en" /> </bean> <bean id="localeChangeInterceptor" class="org.springframework.web.servlet.i18n.LocaleChangeInterceptor"> <property name="paramName" value="lang" /> </bean> <bean class="org.springframework.web.servlet.mvc.annotation.DefaultAnnotationHandlerMapping"> <property name="interceptors"> <list> <ref bean="localeChangeInterceptor" /> </list> </property> </bean> </beans> |
3) JSP changes to display locale specific messages
Next step is to make view changes to support displaying locale specific text messages. This can be done using spring TLDs in below manner.
<%@ page contentType="text/html;charset=UTF-8" %><%@ taglib prefix="c" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/core"%><%@ taglib prefix="fmt" uri="http://java.sun.com/jsp/jstl/fmt"%><%@ taglib prefix="spring" uri="http://www.springframework.org/tags" %><html><head> <title>Spring MVC Hello World</title></head><body> <h2><spring:message code="lbl.page" text="All Employees in System" /></h2> <table border="1"> <tr> <th><spring:message code="lbl.Id" text="Employee Id" /></th> <th><spring:message code="lbl.firstName" text="First Name" /></th> <th><spring:message code="lbl.lastName" text="Last Name" /></th> </tr> <c:forEach items="${employees}" var="employee"> <tr> <td>${employee.id}</td> <td>${employee.firstName}</td> <td>${employee.lastName}</td> </tr> </c:forEach> </table></body></html> |
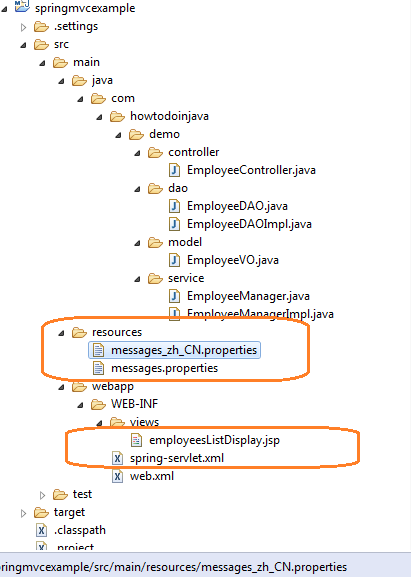
4) Project Structure
The complete structure for this application is this:
5) Testing the Application
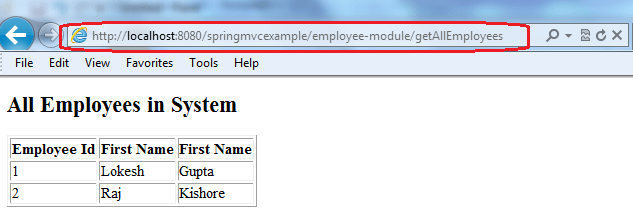
Hit the URL : http://localhost:8080/springmvcexample/employee-module/getAllEmployees
As you see that all labels are displayed in English language.
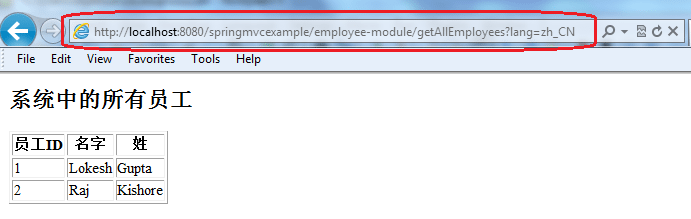
Hit the URL : http://localhost:8080/springmvcexample/employee-module/getAllEmployees?lang=zh_CN
Now, locale has been changed to chinese and all labels are displayed in chinese language.
6) Other Project Files
Let’s list down other files involved into this application.
web.xml
web.xml
<web-app id="WebApp_ID" version="2.4" xmlns="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee" xmlns:xsi="http://www.w3.org/2001/XMLSchema-instance" xsi:schemaLocation="http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee http://java.sun.com/xml/ns/j2ee/web-app_2_4.xsd"> <display-name>Spring Web MVC Hello World Application</display-name> <servlet> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <servlet-class> org.springframework.web.servlet.DispatcherServlet </servlet-class> <load-on-startup>1</load-on-startup> </servlet> <servlet-mapping> <servlet-name>spring</servlet-name> <url-pattern>/</url-pattern> </servlet-mapping></web-app> |
EmployeeController.java
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.controller;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Controller;import org.springframework.ui.Model;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMapping;import org.springframework.web.bind.annotation.RequestMethod;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.service.EmployeeManager;@Controller@RequestMapping("/employee-module")public class EmployeeController { @Autowired EmployeeManager manager; @RequestMapping(value="/getAllEmployees", method = RequestMethod.GET) public String welcome(Model model) { model.addAttribute("employees",manager.getAllEmployees()); return "employeesListDisplay"; }} |
EmployeeDAO.java
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.dao;import java.util.List;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeVO;public interface EmployeeDAO { public List<EmployeeVO> getAllEmployees();} |
EmployeeDAOImpl.java
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.dao;import java.util.ArrayList;import java.util.List;import org.springframework.stereotype.Repository;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeVO;@Repositorypublic class EmployeeDAOImpl implements EmployeeDAO { public List<EmployeeVO> getAllEmployees() { List<EmployeeVO> employees = new ArrayList<EmployeeVO>(); EmployeeVO vo1 = new EmployeeVO(); vo1.setId(1); vo1.setFirstName("Lokesh"); vo1.setLastName("Gupta"); employees.add(vo1); EmployeeVO vo2 = new EmployeeVO(); vo2.setId(2); vo2.setFirstName("Raj"); vo2.setLastName("Kishore"); employees.add(vo2); return employees; }} |
EmployeeManager.java
import java.util.List;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeVO;public interface EmployeeManager { public List<EmployeeVO> getAllEmployees();} |
EmployeeManagerImpl.java
import java.util.List;import org.springframework.beans.factory.annotation.Autowired;import org.springframework.stereotype.Service;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.dao.EmployeeDAO;import com.howtodoinjava.demo.model.EmployeeVO;@Servicepublic class EmployeeManagerImpl implements EmployeeManager { @Autowired EmployeeDAO dao; public List<EmployeeVO> getAllEmployees() { return dao.getAllEmployees(); }} |
EmployeeVO.java
package com.howtodoinjava.demo.model;import java.io.Serializable;public class EmployeeVO implements Serializable { private static final long serialVersionUID = 1L; private Integer id; private String firstName; private String lastName; public Integer getId() { return id; } public void setId(Integer id) { this.id = id; } public String getFirstName() { return firstName; } public void setFirstName(String firstName) { this.firstName = firstName; } public String getLastName() { return lastName; } public void setLastName(String lastName) { this.lastName = lastName; } @Override public String toString() { return "EmployeeVO [id=" + id + ", firstName=" + firstName + ", lastName=" + lastName + "]"; }} |
Please let me know if any queries or thoughts.
No comments:
Post a Comment