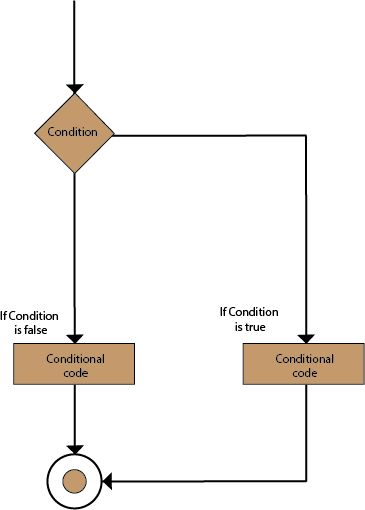
In the if statement, the inner code is executed when the condition is true. The code which is outside the if block will be executed when the if condition is false.
There is another type of decision-making statement known as the if-else statement. An if-else statement is the if statement followed by an else statement. An if-else statement, else statement will be executed when the boolean expression will false. In simple words, If a Boolean expression will have true value, then the if block gets executed otherwise, the else block will get executed.
R programming treats any non-zero and non-null values as true, and if the value is either zero or null, then it treats them as false.
The basic syntax of If-else statement is as follows:
- if(boolean_expression) {
-
- } else {
-
- }
Flow Chart
Example 1
- # local variable definition
- a<- 100
- #checking boolean condition
- if(a<20){
- # if the condition is true then print the following
- cat("a is less than 20\n")
- }else{
- # if the condition is false then print the following
- cat("a is not less than 20\n")
- }
- cat("The value of a is", a)
Output:
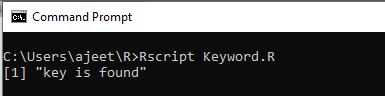
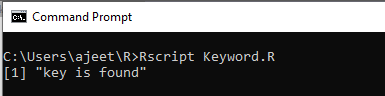
Example 2
- x <- c("Hardwork","is","the","key","of","success")
-
- if("key" %in% x) {
- print("key is found")
- } else {
- print("key is not found")
- }
Output:
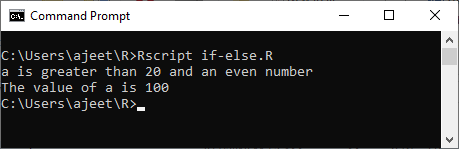
Example 3
- a<- 100
- #checking boolean condition
- if(a<20){
- cat("a is less than 20")
- if(a%%2==0){
- cat(" and an even number\n")
- }
- else{
- cat(" but not an even number\n")
- }
- }else{
- cat("a is greater than 20")
- if(a%%2==0){
- cat(" and an even number\n")
- }
- else{
- cat(" but not an even number\n")
- }
- }
Output:
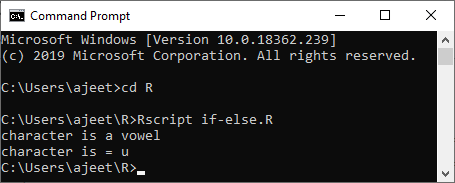
Example 4
- a<- 'u'
- if(a=='a'||a=='e'||a=='i'||a=='o'||a=='u'||a=='A'||a=='E'||a=='I'||a=='O'||a=='U'){
- cat("character is a vowel\n")
- }else{
- cat("character is a constant")
- }
- cat("character is =",a)
- }
Output:
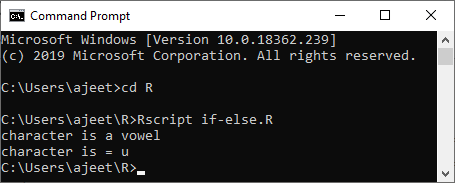
Example 5
- a<- 'u'
- if(a=='a'||a=='e'||a=='i'||a=='o'||a=='u'||a=='A'||a=='E'||a=='I'||a=='O'||a=='U'){
- cat("character is a vowel\n")
- }else{
- cat("character is a constant")
- }
- cat("character is =",a)
- }
Output:






No comments:
Post a Comment