A Spring MVC is a Java framework which is used to build web applications. It follows the Model-View-Controller design pattern. It implements all the basic features of a core spring framework like Inversion of Control, Dependency Injection.
A Spring MVC provides an elegant solution to use MVC in spring framework by the help of DispatcherServlet. Here, DispatcherServlet is a class that receives the incoming request and maps it to the right resource such as controllers, models, and views.
Spring Web Model-View-Controller
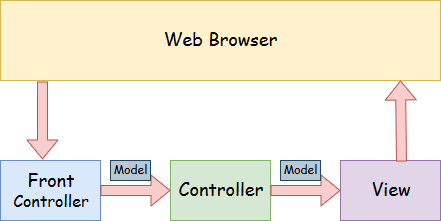
- Model - A model contains the data of the application. A data can be a single object or a collection of objects.
- Controller - A controller contains the business logic of an application. Here, the @Controller annotation is used to mark the class as the controller.
- View - A view represents the provided information in a particular format. Generally, JSP+JSTL is used to create a view page. Although spring also supports other view technologies such as Apache Velocity, Thymeleaf and FreeMarker.
- Front Controller - In Spring Web MVC, the DispatcherServlet class works as the front controller. It is responsible to manage the flow of the Spring MVC application.
Understanding the flow of Spring Web MVC
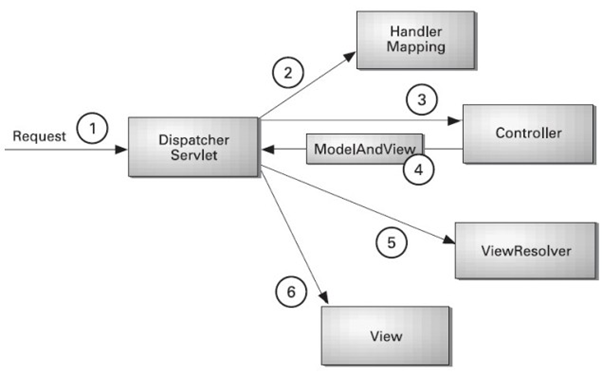
- As displayed in the figure, all the incoming request is intercepted by the DispatcherServlet that works as the front controller.
- The DispatcherServlet gets an entry of handler mapping from the XML file and forwards the request to the controller.
- The controller returns an object of ModelAndView.
- The DispatcherServlet checks the entry of view resolver in the XML file and invokes the specified view component.
Advantages of Spring MVC Framework
Let's see some of the advantages of Spring MVC Framework:-
- Separate roles - The Spring MVC separates each role, where the model object, controller, command object, view resolver, DispatcherServlet, validator, etc. can be fulfilled by a specialized object.
- Light-weight - It uses light-weight servlet container to develop and deploy your application.
- Powerful Configuration - It provides a robust configuration for both framework and application classes that includes easy referencing across contexts, such as from web controllers to business objects and validators.
- Rapid development - The Spring MVC facilitates fast and parallel development.
- Reusable business code - Instead of creating new objects, it allows us to use the existing business objects.
- Easy to test - In Spring, generally we create JavaBeans classes that enable you to inject test data using the setter methods.
- Flexible Mapping - It provides the specific annotations that easily redirect the page.
Spring Web MVC Framework Example
Let's see the simple example of a Spring Web MVC framework. The steps are as follows:
- Load the spring jar files or add dependencies in the case of Maven
- Create the controller class
- Provide the entry of controller in the web.xml file
- Define the bean in the separate XML file
- Display the message in the JSP page
- Start the server and deploy the project
Directory Structure of Spring MVC
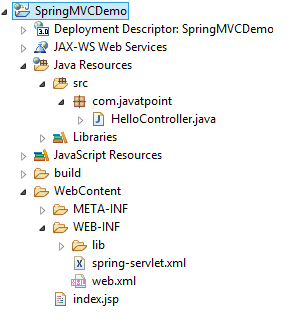
Directory Structure of Spring MVC using Maven
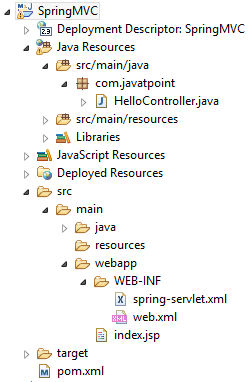
Required Jar files or Maven Dependency
To run this example, you need to load:
- Spring Core jar files
- Spring Web jar files
- JSP + JSTL jar files (If you are using any another view technology then load the corresponding jar files).
Download Link: Download all the jar files for spring including JSP and JSTL.
If you are using Maven, you don't need to add jar files. Now, you need to add maven dependency to the pom.xml file.
1. Provide project information and configuration in the pom.xml file.
pom.xml
2. Create the controller class
To create the controller class, we are using two annotations @Controller and @RequestMapping.
The @Controller annotation marks this class as Controller.
The @Requestmapping annotation is used to map the class with the specified URL name.
HelloController.java
3. Provide the entry of controller in the web.xml file
In this xml file, we are specifying the servlet class DispatcherServlet that acts as the front controller in Spring Web MVC. All the incoming request for the html file will be forwarded to the DispatcherServlet.
web.xml
4. Define the bean in the xml file
This is the important configuration file where we need to specify the View components.
The context:component-scan element defines the base-package where DispatcherServlet will search the controller class.
This xml file should be located inside the WEB-INF directory.
spring-servlet.xml
5. Display the message in the JSP page
This is the simple JSP page, displaying the message returned by the Controller.
index.jsp
Output:
No comments:
Post a Comment