A variable is a container which holds the value while the java program is executed. A variable is assigned with a datatype.
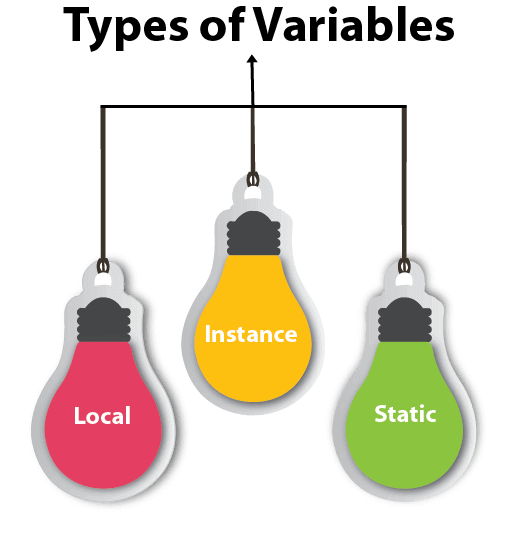
Variable is a name of memory location. There are three types of variables in java: local, instance and static.
There are two types of data types in java: primitive and non-primitive.
Variable
Variable is name of reserved area allocated in memory. In other words, it is a name of memory location. It is a combination of "vary + able" that means its value can be changed.
Types of Variables
There are three types of variables in java:
- local variable
- instance variable
- static variable
1) Local Variable
A variable declared inside the body of the method is called local variable. You can use this variable only within that method and the other methods in the class aren't even aware that the variable exists.
A local variable cannot be defined with "static" keyword.
2) Instance Variable
A variable declared inside the class but outside the body of the method, is called instance variable. It is not declared as static.
It is called instance variable because its value is instance specific and is not shared among instances.
3) Static variable
A variable which is declared as static is called static variable. It cannot be local. You can create a single copy of static variable and share among all the instances of the class. Memory allocation for static variable happens only once when the class is loaded in the memory.
Example to understand the types of variables in java
Java Variable Example: Add Two Numbers
Output:
20
Java Variable Example: Widening
Output:
10 10.0
Java Variable Example: Narrowing (Typecasting)
Output:
10.5 10
Java Variable Example: Overflow
Output:
130 -126
Java Variable Example: Adding Lower Type
Output:
20
No comments:
Post a Comment