iOS Location Services (Get User Location Details)
In iOS we can get user location details like latitude, longitude and current location address of the user by using core location framework in swift applications.
The core location framework in iOS provides a several location services to get and track the device current location.
We can get current device location details in our iOS applications by using Core Location Framework reference. Now we will see how to get users current location details in our iOS applications using swift with example.
Create iOS Location Services App in Swift
To create new project in iOS open Xcode from /Applications folder directory. Once we open Xcode the welcome window will open like as shown below. In welcome window click on the second option “Create a new Xcode Project” or choose File à New à Project.
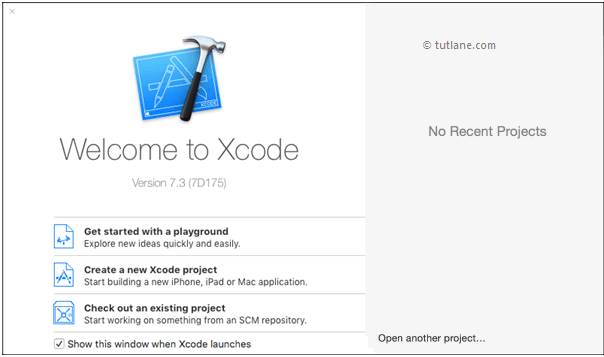
After selecting “Create a new Xcode project” a new window will open in that we need to choose template.
The new Xcode window will contain several built-in app templates to implement common type of iOS apps like page based apps, tab-based apps, games, table-view apps, etc. These templates are having pre-configured interface and source code files.
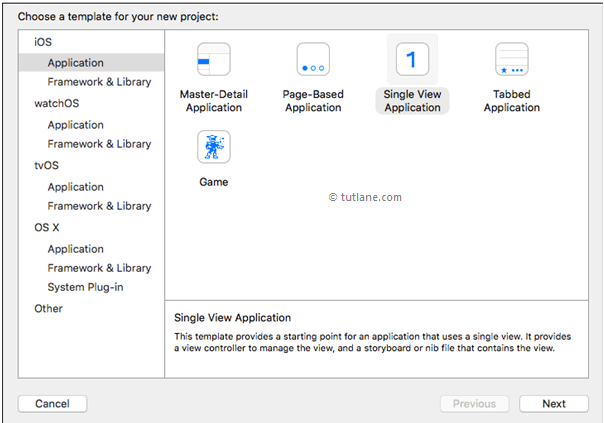
For this iOS Location example, we will use most basic template “Single View Application”. To select this one, Go to the iOS section in left side à select Application à In main area of dialog select “Single View Application” and then click on next button like as shown below.
After click Next we will get window like as shown below, in this we need to mention project name and other details for our application.
Product Name: “MyLocations”
The name whatever we enter in Product Name section will be used for the project and app.
Organization Name: “Tutlane”
You can enter the name of your organization or your own name or you can leave it as blank.
Organization Identifier: “com.developersociety”
Enter your organization identifier in case if you don't have any organization identifier enter com.example.
Bundle Identifier: This value will generate automatically based on the values we entered in Product Name and Organization Identifier.
Language: “Swift”
Select language type as “Swift” because we are going to develop applications using swift.
Devices: “Universal”
Choose Devices options as Universal it means that one application is for all apple devices in case if you have any specific requirement to run app only for iPad then you can choose the iPad option to make your application restricted to run only on iPad devices.
Use Core Data: Unselected
This option is used for database operations. In case if you have any database related operations in your application select this option otherwise unselect the option.
Include Unit Tests: Unselected
In case if you need unit tests for your application then select this option otherwise unselect it.
Include UI Tests: Unselected
In case if you need UI tests for your application then select this option otherwise unselect it.
Once you finished entering all the options then click on Next button like as shown below.

Once we click on Next button new dialog will open in that we need to select the location to save our project. Once you select the location to save project then click on Create button like as shown below
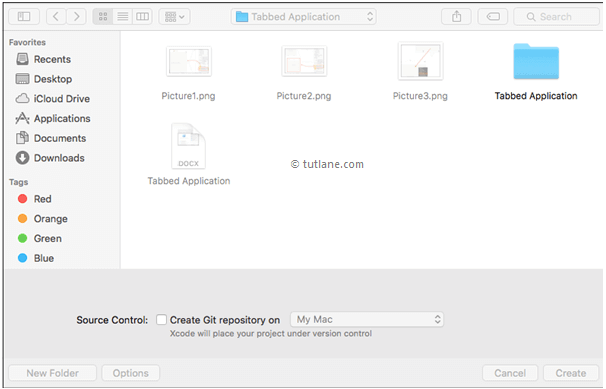
After click on Create button the Xcode will create and open a new project. In our project Main.storyboard and ViewController.swift are the main files which we used to design app user interface and to maintain source code.
Main.storyboard - Its visual interface editor and we will use this file to design our app user interface
ViewController.swift - It contains source code of our application and we use this file to write any code related to our app.
Now in project select Main.storyboard file the Xcode will open visual interface editor like as shown below.

Now select ViewController.swift file in your project that view will be like as shown below.

Now click on Project à Go to the Build Phases à Click on + button and search for Core Location and add framework into your project like as shown below

Add iOS UI Controls to View in Swift
Now we will add controls to our application for that open Object Library. The Object Library will appear at the bottom of Xcode in right side. In case if you don't find Object library, click on the button which is at the third position from the left in the library selector bar like as shown below. (Alternatively you can choose View à Utilities à Show Object Library.)

As we discussed our user interface will be in Main.storyboard file so open Main.storyboard file. Now in Object library search for the label in Filter field then drag and drop the label into Main.storyboard ViewController like as shown below same way we need to add multiple labels and one button control in our ViewController file.

Connect iOS UI Controls to Code in Swift
Now we will make connection between controls and ViewController.Swift code for that click on assistant button (overlap circle) in Xcode toolbar right side corner like as shown below.

To map the controls, press Ctrl button in keyboard and drag all labels and button from view controller and drop into ViewController.swift file like as shown below

Once we done with settings we need to write custom code to get current user location details in ViewController.swift file like as shown below
import UIKit
import CoreLocation
class CurrentLocationViewController: UIViewController, CLLocationManagerDelegate {
@IBOutlet weak var messageLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var latitudeLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var longitudeLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var addressLabel: UILabel!
@IBOutlet weak var tagButton: UIButton!
@IBOutlet weak var getButton: UIButton!
let locationManager = CLLocationManager()
var location: CLLocation?
var updatingLocation = false
var lastLocationError: NSError?
let geocoder = CLGeocoder()
var placemark: CLPlacemark?
var performingReverseGeocoding = false
var lastGeocodingError: NSError?
var timer: NSTimer?
@IBAction func getLocation() {
let authStatus = CLLocationManager.authorizationStatus()
if authStatus == .NotDetermined {
locationManager.requestWhenInUseAuthorization()
return
}
if authStatus == .Denied || authStatus == .Restricted {
showLocationServicesDeniedAlert()
return
}
if updatingLocation {
stopLocationManager()
} else {
location = nil
lastLocationError = nil
placemark = nil
lastGeocodingError = nil
startLocationManager()
}
updateLabels()
configureGetButton()
}
override func viewDidLoad() {
super.viewDidLoad()
updateLabels()
configureGetButton()
}
override func didReceiveMemoryWarning() {
super.didReceiveMemoryWarning()
// Dispose of any resources that can be recreated.
}
func showLocationServicesDeniedAlert() {
let alert = UIAlertController(title: "Location Services Disabled",
message: "Please enable location services for this app in Settings.",
preferredStyle: .Alert)
let okAction = UIAlertAction(title: "OK", style: .Default, handler: nil)
alert.addAction(okAction)
presentViewController(alert, animated: true, completion: nil)
}
func startLocationManager() {
if CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled() {
locationManager.delegate = self
locationManager.desiredAccuracy = kCLLocationAccuracyNearestTenMeters
locationManager.startUpdatingLocation()
updatingLocation = true
timer = NSTimer.scheduledTimerWithTimeInterval(60, target: self, selector: #selector(CurrentLocationViewController.didTimeOut), userInfo: nil, repeats: false)
}
}
func stopLocationManager() {
if updatingLocation {
locationManager.stopUpdatingLocation()
locationManager.delegate = nil
updatingLocation = false
if let timer = timer {
timer.invalidate()
}
}
}
func didTimeOut() {
print("*** Time out")
if location == nil {
stopLocationManager()
lastLocationError = NSError(domain: "MyLocationsErrorDomain", code: 1, userInfo: nil)
updateLabels()
configureGetButton()
}
}
func updateLabels() {
if let location = location {
latitudeLabel.text = String(format: "%.8f", location.coordinate.latitude)
longitudeLabel.text = String(format: "%.8f", location.coordinate.longitude)
tagButton.hidden = false
messageLabel.text = ""
if let placemark = placemark {
addressLabel.text = stringFromPlacemark(placemark)
} else if performingReverseGeocoding {
addressLabel.text = "Searching for Address..."
} else if lastGeocodingError != nil {
addressLabel.text = "Error Finding Address"
} else {
addressLabel.text = "No Address Found"
}
} else {
latitudeLabel.text = ""
longitudeLabel.text = ""
addressLabel.text = ""
tagButton.hidden = true
let statusMessage: String
if let error = lastLocationError {
if error.domain == kCLErrorDomain && error.code == CLError.Denied.rawValue {
statusMessage = "Location Services Disabled"
} else {
statusMessage = "Error Getting Location"
}
} else if !CLLocationManager.locationServicesEnabled() {
statusMessage = "Location Services Disabled"
} else if updatingLocation {
statusMessage = "Searching..."
} else {
statusMessage = "Tap 'Get My Location' to Start"
}
messageLabel.text = statusMessage
}
}
func stringFromPlacemark(placemark: CLPlacemark) -> String {
var line1 = ""
if let s = placemark.subThoroughfare {
line1 += s + " "
}
if let s = placemark.thoroughfare {
line1 += s
}
var line2 = ""
iflet s = placemark.locality {
line2 += s + " "
}
if let s = placemark.administrativeArea {
line2 += s + " "
}
if let s = placemark.postalCode {
line2 += s
}
return line1 + "\n" + line2
}
func configureGetButton() {
if updatingLocation {
getButton.setTitle("Stop", forState: .Normal)
} else {
getButton.setTitle("Get My Location", forState: .Normal)
}
}
override func prepareForSegue(segue: UIStoryboardSegue, sender: AnyObject?) {
if segue.identifier == "TagLocation" {
let navigationController = segue.destinationViewController as! UINavigationController
let controller = navigationController.topViewController as! LocationDetailsViewController
controller.coordinate = location!.coordinate
controller.placemark = placemark
}
}
// MARK: - CLLocationManagerDelegate
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didFailWithError error: NSError) {
print("didFailWithError \(error)")
if error.code == CLError.LocationUnknown.rawValue {
return
}
lastLocationError = error
stopLocationManager()
updateLabels()
configureGetButton()
}
func locationManager(manager: CLLocationManager, didUpdateLocations locations: [CLLocation]) {
let newLocation = locations.last!
print("didUpdateLocations \(newLocation)")
if newLocation.timestamp.timeIntervalSinceNow < -5 {
return
}
if newLocation.horizontalAccuracy < 0 {
return
}
var distance = CLLocationDistance(DBL_MAX)
if let location = location {
distance = newLocation.distanceFromLocation(location)
}
if location == nil || location!.horizontalAccuracy > newLocation.horizontalAccuracy {
lastLocationError = nil
location = newLocation
updateLabels()
if newLocation.horizontalAccuracy <= locationManager.desiredAccuracy {
print("*** We're done!")
stopLocationManager()
configureGetButton()
if distance > 0 {
performingReverseGeocoding = false
}
}
if !performingReverseGeocoding {
print("*** Going to geocode")
performingReverseGeocoding = true
geocoder.reverseGeocodeLocation(newLocation, completionHandler: {
placemarks, error in
//print("*** Found placemarks: \(placemarks), error: \(error)")
self.lastGeocodingError = error
if error == nil, let p = placemarks where !p.isEmpty {
self.placemark = p.last!
} else {
self.placemark = nil
}
self.performingReverseGeocoding = false
self.updateLabels()
})
}
} else if distance < 1.0 {
let timeInterval = newLocation.timestamp.timeIntervalSinceDate(location!.timestamp)
if timeInterval > 10 {
print("*** Force done!")
stopLocationManager()
updateLabels()
configureGetButton()
}
}
}
}
Now we will run and check the output of application. To run application, select the required simulator (Here we selected iPhone 6s Plus) and click on Play button, located at the top-left corner of the Xcode toolbar like as shown below.

Output of iOS Location App in Swift
Following is the result of iOS Location application in swift. Now click on “Get My Location” button to get user longitude, latitude and current position along with address.

This is how we can use iOS location services in swift applications to get user current locations like latitude, longtitude, address, etc. based on our requirement.
No comments:
Post a Comment